Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Crude Pollen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ultrasonic Extraction Procedure
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.2.2. Total Flavone Content (TFC)
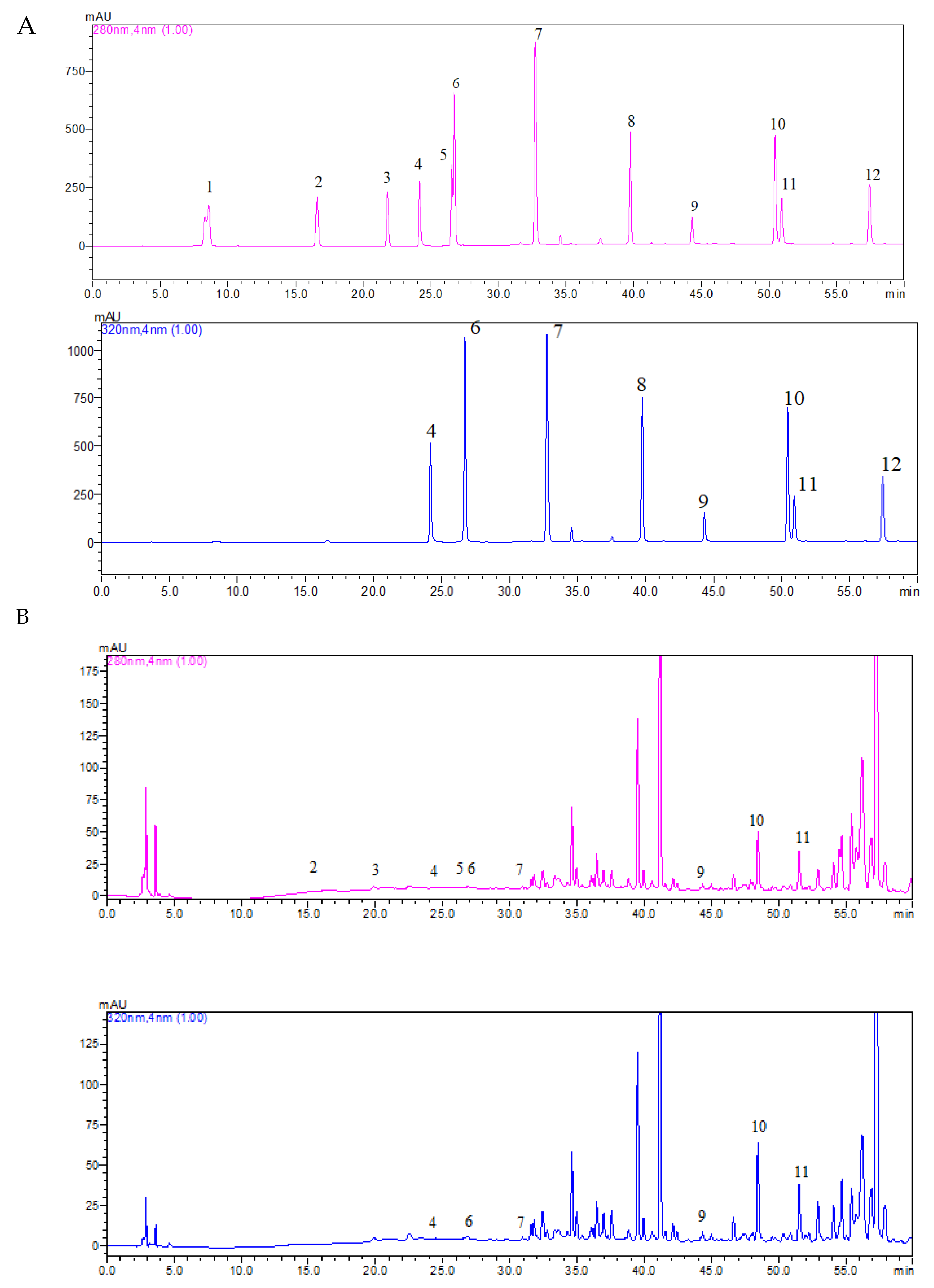
2.2.3. Individual Phenolics Separation and Detection
2.2.4. GC Analysis of Fatty Acids Methyl Esters
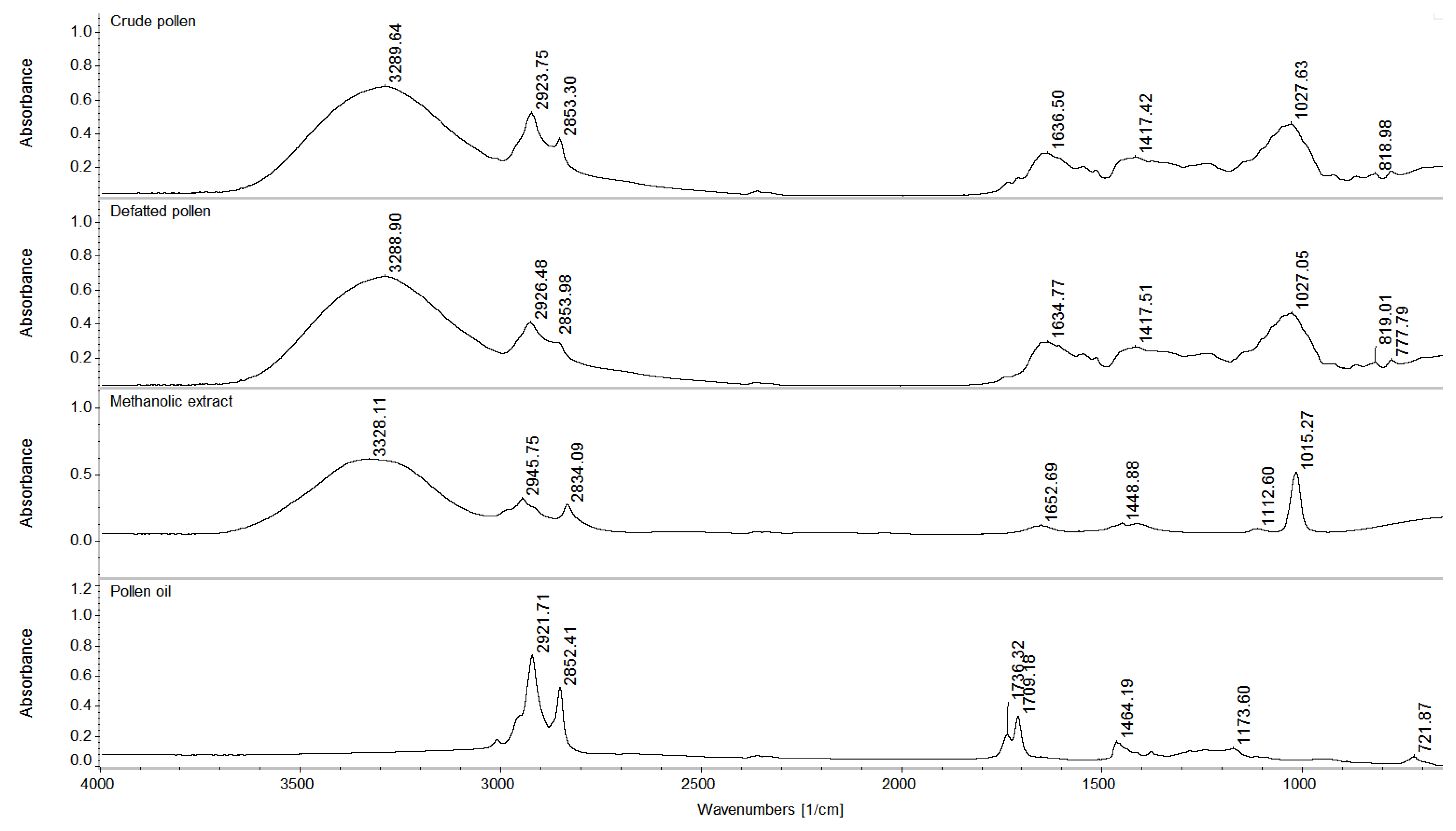
2.2.5. FT-IR
2.2.6. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Ultrasonic Amplitude
3.2. Influence of Solid/Liquid Ratio
3.3. Influence of Extraction Temperature
3.4. Influence of Extraction Time
3.5. Extraction Modeling
3.6. Extraction Yield
3.7. Optimization of Extraction Parameters and Validation of the Models
3.8. Composition of Individual Phenolics
3.9. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.10. Fatty Acid Composition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basim, E.; Basim, H.; Özcan, M. Antibacterial activities of Turkish pollen and propolis extracts against plant bacterial pathogens. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Muradian, L.; Pamplona, L.C.; Coimbra, S.; Barth, O.M. Chemical composition and botanical evaluation of dried bee pollen pellets. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2005, 18, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.; Iglesias, A.; Feás, X.; Estevinho, L.M. Commercial Bee Pollen with Different Geographical Origins: A Comprehensive Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11173–11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardana, C.; Del Bo’, C.; Quicazan, M.; Corrrea, A.R.; Simonetti, P. Nutrients, phytochemicals and botanical origin of commercial bee pollen from different geographical areas. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 73, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.S.; Chambó, E.D.; Costa, M.A.P.D.C.; Da Silva, S.C.; De Carvalho, C.L.; Estevinho, L.M.; Da Silva, S.M.P.C.; De Carvalho, C.A.L. Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Mono- and Heterofloral Bee Pollen of Different Geographical Origins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzepecka-Stojko, A.; Stojko, J.; Kurek-Górecka, A.; Górecki, M.; Kabała-Dzik, A.; Kubina, R.; Moździerz, A.; Buszman, E. Polyphenols from Bee Pollen: Structure, Absorption, Metabolism and Biological Activity. Molecules 2015, 20, 21732–21749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatrcová-Šramková, K.; Nôžková, J.; Máriássyová, M.; Kačániová, M. Biologically active antimicrobial and antioxidant substances in theHelianthus annuusL. bee pollen. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part B 2015, 51, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mărgăoan, R.; Mărghitaş, L.A.; Dezmirean, D.S.; Dulf, F.V.; Bunea, A.; Socaci, S.A.; Bobis, O. Predominant and Secondary Pollen Botanical Origins Influence the Carotenoid and Fatty Acid Profile in Fresh Honeybee-Collected Pollen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6306–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marić, M.; Grassino, A.N.; Zhu, Z.; Barba, F.J.; Brnčić, M.; Brnčić, S.R. An overview of the traditional and innovative approaches for pectin extraction from plant food wastes and by-products: Ultrasound-, microwaves-, and enzyme-assisted extraction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Meullemiestre, A.; Turk, M.; Perino, S.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Abert-Vian, M. Review of Green Food Processing techniques. Preservation, transformation, and extraction. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.L. Pectin. In Handbook of Dietary Fiber, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; Chapter 30; pp. 566–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.-G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Vian, M.A. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, I.G.; Maran, J.P.; Ilakya, S.; Anitha, S.; Sabarima, S.P.; Priya, B. Ultrasound assisted extraction of pectin from waste Artocarpus heterophyllus fruit peel. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2017, 34, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of total monomeric anthocyanin (TMA) and total phenolic content (TPC) from eggplant ( Solanum melongena L.) peel. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2016, 31, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wang, K.; Qiao, J.; Dong, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H. Improving nutrient release of wall-disrupted bee pollen with a combination of ultrasonication and high shear technique. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.-L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, R. Effect of ultrasonic and ball-milling treatment on cell wall, nutrients, and antioxidant capacity of rose (Rosa rugosa) bee pollen, and identification of bioactive components. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5350–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escriche, I.; Juan-Borrás, M. Standardizing the analysis of phenolic profile in propolis. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, M.P.; Giannopoulou, E.; Bogdanov, S.; Tsvetkova, I.; Naydenski, C.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Sabatini, A.-G. Chemical characteristics of poplar type propolis of different geographic origin. Apidologie 2007, 38, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, I.; Lozano, M.; Moro, C.; D’Arrigo, M.; Rostagno, M.A.; Martinez, J.; García-Lafuente, A.; Guillamón, E.; Villares, A. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds occurring in edible mushrooms. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroian, M.; Dranca, F.; Ursachi, F. Comparative evaluation of maceration, microwave and ultrasonic-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from propolis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 57, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroian, M.; Ursachi, F.; Dranca, F. Influence of ultrasonic amplitude, temperature, time and solvent concentration on bioactive compounds extraction from propolis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 64, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulf, F.V. Fatty acids in berry lipids of six sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L., subspecies carpatica) cultivars grown in Romania. Chem. Central J. 2012, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maran, J.P.; Manikandan, S.; Nivetha, C.V.; Dinesh, R. Ultrasound assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from Nephelium lappaceum L. fruit peel using central composite face centered response surface design. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1145–S1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Porto, C.; Porretto, E.; Decorti, D. Comparison of ultrasound-assisted extraction with conventional extraction methods of oil and polyphenols from grape (Vitis vinifera L.) seeds. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2013, 20, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan Van, M.; Tran Anh, V.; Tran Chi, H. Effect of ultrasound on extraction of polyphenol from the old tea leaves. Ann. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 18, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Oladejo, A.O.; Ruan, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Ma, H. Effects of ultrasound pretreatment with different frequencies and working modes on the enzymolysis and the structure characterization of rice protein. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2017, 38, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzah, C.S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Ma, H. The effects of ultrasound assisted extraction on yield, antioxidant, anticancer and antimicrobial activity of polyphenol extracts: A review. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussios, C.C.; Farny, C.H.; Ter Haar, G.; Roy, R. Role of acoustic cavitation in the delivery and monitoring of cancer treatment by high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU). Int. J. Hyperth. 2007, 23, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyaningsih, W.; Saputro, I.E.; Carrera, C.; Ferreiro-González, M. Optimisation of an ultrasound-assisted extraction method for the simultaneous determination of phenolics in rice grains. Food Chem. 2019, 288, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.G.; De Almeida, P.H.; Oliveira, T.L.; Silva, L.D.S.; De Carvalho, F.S.; Alves, S.F.; Borges, L.L.; Dos Santos, P.A.; Da Silva, V.B.; De Paula, J.R. HPLC-PDA method validated for the determination of hibalactone in Hydrocotyle umbellata subterraneous parts and its ultrasound-assisted extraction optimization. Rev. Bras. de Farm. 2019, 29, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlić, B.; Kaplan, M.; Bera, O.; Olgun, E.O.; Canli, O.; Milosavljević, N.; Antić, B.; Zeković, Z. Microwave-assisted extraction of peppermint polyphenols—Artificial neural networks approach. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 118, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Turner, C. Pressurized liquid extraction as a green approach in food and herbal plants extraction: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 703, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara-Salinas, J.R.; Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Torres, J.L.; Agosin, E.; Pérez-Correa, J.R. Effects of Temperature and Time on Polyphenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity in the Pressurized Hot Water Extraction of Deodorized Thyme (Thymus vulgaris). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10920–10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, A.A.; Đorđević, V.B.; Zdunić, G.; Pljevljakusic, D.; Šavikin, K.P.; Gođevac, D.M.; Bugarski, B.M. Optimization of the extraction process of polyphenols from Thymus serpyllum L. herb using maceration, heat- and ultrasound-assisted techniques. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, M.; Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Penić, M.; Brñić, M.; Bosiljkov, T.; Levaj, B. The effect of extraction solvents, temperature and time on the composition and mass fraction of polyphenols in dalmatian wild sage (Salvia officinalis L.) extracts. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 51, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Miron, T.; Plaza, M.; Bahrim, G.; Ibanez, E.; Herrero, M. Chemical composition of bioactive pressurized extracts of Romanian aromatic plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4918–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Total Monomeric Anthocyanin, Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts from Eggplant (Solanum Melongena L.) Peel Using Ultrasonic Treatments. J. Food Process. Eng. 2015, 40, e12312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L.; Talmaciu, A.I.; Volf, I.; Popa, V.I. Kinetic modeling of the ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols from Picea abies bark. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2016, 32, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goula, A.M.; Thymiatis, K.; Kaderides, K. Valorization of grape pomace: Drying behavior and ultrasound extraction of phenolics. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Wang, L.-J.; Li, D.; Jiao, S.-S.; Chen, X.D.; Mao, Z.-H. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of oil from flaxseed. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, A.; Malika, D.; Bakari, S.; Hfaiedh, N.; Mnafgui, K.; Kadri, A.; Gharsallah, N. Assessment of polyphenol composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of various extracts of Date Palm Pollen (DPP) from two Tunisian cultivars. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 3075–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostić, A.Ž.; Mačukanović-Jocić, M.P.; Trifunović, B.Š.; Vukašinović, I.; Pavlović, V.; Pešić, M.B. Fatty acids of maize pollen–Quantification, nutritional and morphological evaluation. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 77, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilić, S.; Vančetović, J.; Janković, M.; Maksimović, V.M. Chemical composition, bioactive compounds, antioxidant capacity and stability of floral maize (Zea mays L.) pollen. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, S.; Astolfi, P.; Conti, C.; Monaci, E.; Stefano, M.; Carloni, P. Morphological, Physicochemical and FTIR Spectroscopic Properties of Bee Pollen Loads from Different Botanical Origin. Molecules 2019, 24, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Anjos, O.M.S.; A Santos, A.J.; Dias, T.; Estevinho, L.M. Application of FTIR-ATR spectroscopy on the bee pollen characterization. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Nanda, V. Composition and functionality of bee pollen: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 82–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, I.; Depciuch, J.; Grabek-Lejko, D.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M. FTIR-ATR spectroscopy of pollen and honey as a tool for unifloral honey authentication. The case study of rape honey. Food Control. 2018, 84, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-L.; Zheng, Y.-Z.; Chen, X.-C.; Zhu, F.-L.; Miao, X.-Q. Identification of cattail pollen, pine pollen and bee pollen by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1167, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, P.; Abernethy, F.A.; Lomax, B.H.; Gosling, W.D.; Fraser, W. Shedding light on sporopollenin chemistry, with reference to UV reconstructions. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2017, 238, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos, O.M.S.; Campos, M.D.G.R.; Ruiz, P.C.; Antunes, P. Application of FTIR-ATR spectroscopy to the quantification of sugar in honey. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.; Kohler, A. Infrared Spectroscopy of Pollen Identifies Plant Species and Genus as Well as Environmental Conditions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belina-Aldemita, M.D.; Opper, C.; Schreiner, M.; D’Amico, S. Nutritional composition of pot-pollen produced by stingless bees (Tetragonula biroi Friese) from the Philippines. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 82, 103215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2003, 916, 1–149. [Google Scholar]
| Independent Variables | Coded Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Ultrasonic amplitude (%) – X1 | 20 | 60 | 100 |
| Solid liquid ratio | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Temperature (°C) – X3 | 35 | 50 | 65 |
| Time (min) – X4 | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Parameter | Ultrasonic Amplitude (%) | F Value | Solid Liquid Ratio (g/L) | F Value | Temperature (°C) | F Value | Time (min) | F Value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 60 | 100 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 35 | 50 | 65 | 10 | 20 | 30 | |||||
| Extraction yield (%) | 1.23 c | 1.25 b | 1.29 a | 15.4 *** | 0.64 c | 1.25 b | 1.89 a | 7439 *** | 1.24 b | 1.24 b | 1.30 a | 14.3 ** | 1.25 a | 1.27 a | 1.26 a | 0.08 ns |
| TPC (mg GAE/L) | 221 b | 222 b | 277 a | 17.5 *** | 164 c | 233 b | 323 a | 128 *** | 216 a | 250 a | 254 a | 0.75 ns | 238 a | 244 a | 247 a | 0.23 ns |
| TFC (mg QE/L) | 346 a | 359 a | 441 b | 11.4 ** | 197 c | 402 b | 547 a | 157 *** | 397 a | 389 a | 360 a | 1.78 ns | 406 a | 392 a | 348 a | 4.34 ns |
| Source | DF | Extraction yield (%) | TPC (mg GAE/L) | TFC (mg QE/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | ||
| Model | 14.0 | 534.7 | <0.0001 | 11.63 | <0.0001 | 13.73 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 1.00 | 15.4 | 0.0015 | 17.52 | 0.0009 | 11.40 | 0.0045 |
| X2 | 1.00 | 7439 | <0.0001 | 128.2 | <0.0001 | 157.3 | <0.0001 |
| X3 | 1.00 | 14.3 | 0.0020 | 0.75 | 0.3998 | 1.78 | 0.2035 |
| X4 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.7794 | 0.23 | 0.6390 | 4.34 | 0.0559 |
| X12 | 1.00 | 0.44 | 0.5187 | 2.74 | 0.1198 | 3.36 | 0.0881 |
| X13 | 1.00 | 2.78 | 0.1175 | 3.04 | 0.1030 | 2.42 | 0.1420 |
| X14 | 1.00 | 5.53 | 0.0339 | 9.43 | 0.0083 | 0.27 | 0.6091 |
| X23 | 1.00 | 1.64 | 0.2207 | 1.50 | 0.2413 | 0.58 | 0.4577 |
| X24 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 0.4622 | 3.21 | 0.0946 | 1.62 | 0.2241 |
| X34 | 1.00 | 1.60 | 0.2265 | 0.01 | 0.9273 | 0.40 | 0.5390 |
| 1.00 | 0.18 | 0.6781 | 0.56 | 0.4661 | 2.21 | 0.1590 | |
| 1.00 | 0.06 | 0.8074 | 0.48 | 0.4981 | 3.40 | 0.0864 | |
| 1.00 | 0.01 | 0.9110 | 0.02 | 0.8946 | 0.10 | 0.7547 | |
| 1.00 | 3.09 | 0.1005 | 0.11 | 0.7398 | 1.72 | 0.2112 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.93 | ||||
| Adj-R2 | 0.98 | 0.84 | 0.86 | ||||
| CV% | 1.99 | 13.1 | 12.50 | ||||
| Adeq.Pre | 72.6 | 13.62 | 12.84 | ||||
| Compound | Molecular Weight | Wavelength (nm) | Retention Time (min) | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 170.12 | 280 | 8.617 | ND |
| Protocatechuic acid | 154.12 | 280 | 15.833 | 6.58 |
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 138.12 | 280 | 20.686 | 0.73 |
| Vanillic acid | 168.14 | 280 | 25.400 | 0.31 |
| Caffeic acid | 180.16 | 320 | 23.103 | 2.41 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 354.31 | 320 | 25.605 | 3.35 |
| p-Coumaric acid | 164.05 | 320 | 31.653 | 2.23 |
| Rosmarinic acid | 360.31 | 320 | 39.397 | ND |
| Myricetin | 318.24 | 320 | 43.225 | 20.54 |
| Luteolin | 286.24 | 320 | 49.691 | 5.79 |
| Quercetin | 302.24 | 320 | 50.173 | 10.51 |
| Kaempferol | 286.23 | 320 | 56.558 | ND |
| Fatty Acid | Concentration (µg × g−1 pollen) |
|---|---|
| Myristic acid 14:0 | 159.10 |
| cis-14-Pentadecenoic acid 15:1ωc | 106.61 |
| Palmitic acid 16:0 | 80.51 |
| trans-9-Elaidic acid 18:1ωt | 78.01 |
| Hexanoic acid 6:0 | 46.93 |
| Stearic acid 18:0 | 38.82 |
| z-11-Tetradecenoic acid 14:1ωc | 21.70 |
| Pentadecanoic acid 15:0 | 21.20 |
| Butyric acid 4:0 | 20.88 |
| cis-9-Oleic acid 18:1ωc | 18.05 |
| Palmitoleic acid 16:1 | 15.98 |
| Myristoleic acid 14:1 | 14.57 |
| Octanoic acid 8:0 | 14.13 |
| Linoleic acid 18:2ω6c | 11.63 |
| Eicosanoic acid C:20 | 9.68 |
| Decanoic acid 10:0 | 8.60 |
| Tridecanoic acid 13:0 | 8.10 |
| 11-Eicosenoic acid 20:1 | 6.66 |
| Erucic acid 22:1 | 6.36 |
| Heptadecanoaic acid 17:0 | 6.18 |
| Lignoceric acid 24:0 | 2.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oroian, M.; Ursachi, F.; Dranca, F. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Crude Pollen. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040322
Oroian M, Ursachi F, Dranca F. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Crude Pollen. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(4):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040322
Chicago/Turabian StyleOroian, Mircea, Florin Ursachi, and Florina Dranca. 2020. "Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Crude Pollen" Antioxidants 9, no. 4: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040322
APA StyleOroian, M., Ursachi, F., & Dranca, F. (2020). Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Crude Pollen. Antioxidants, 9(4), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040322





